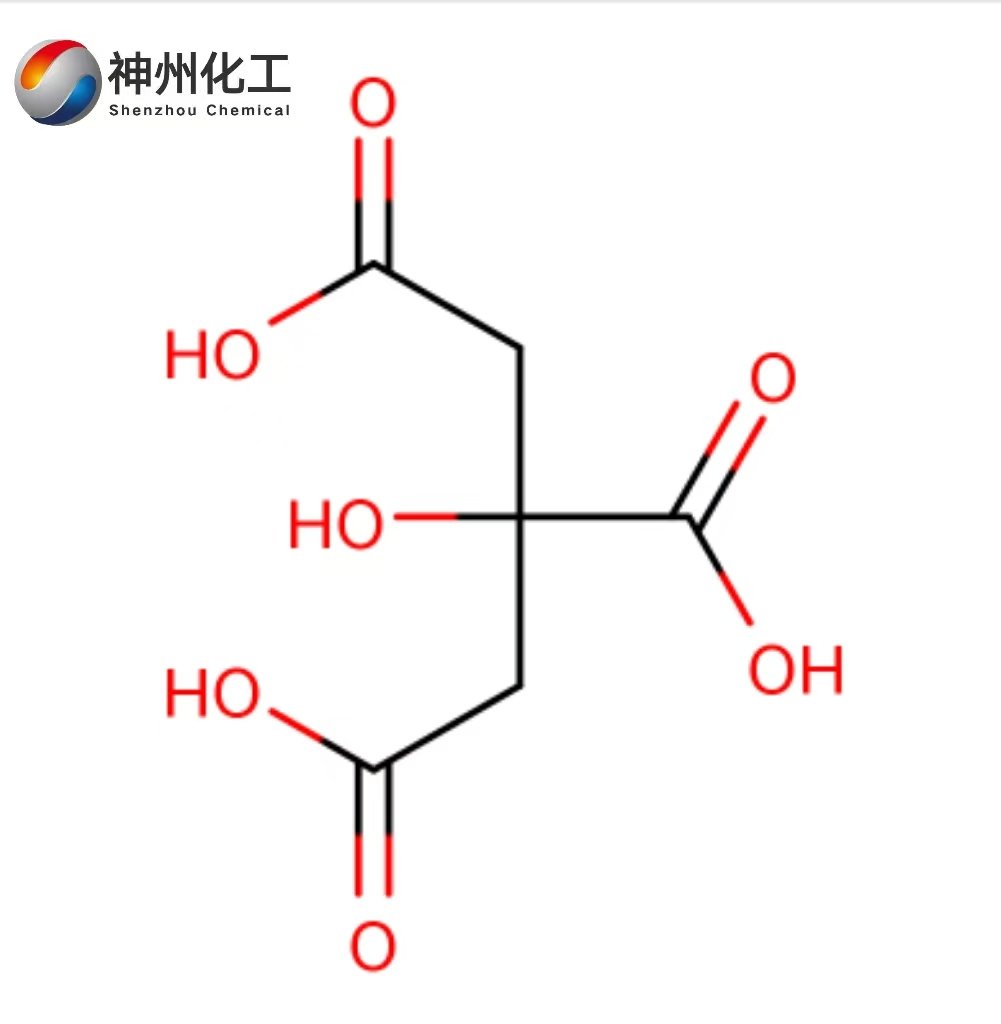
Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9
Have Any Questions?
Let our vertically integrated solutions – from Chinese manufacturing hubs to your local warehouse – become your competitive advantage.
- +86 13376344351
Leave Your Message
Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9

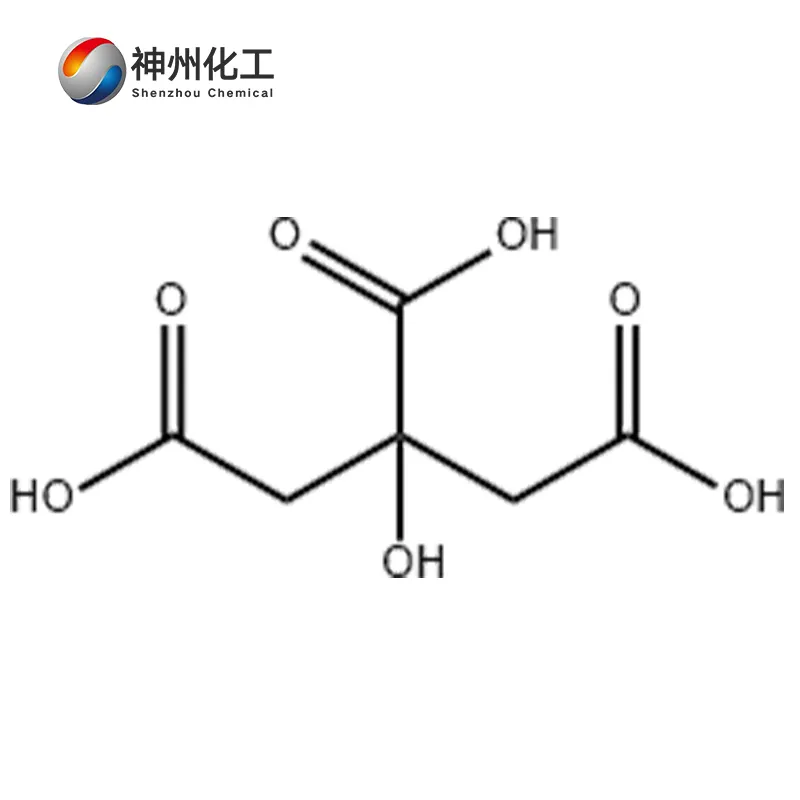


- Chemical Name:Citric Acid Anhydrous
- CAS No.:77-92-9
- Product Categories:Food Additives
- Molecular Formula:C6H8O7
- Formula Weight:192.12
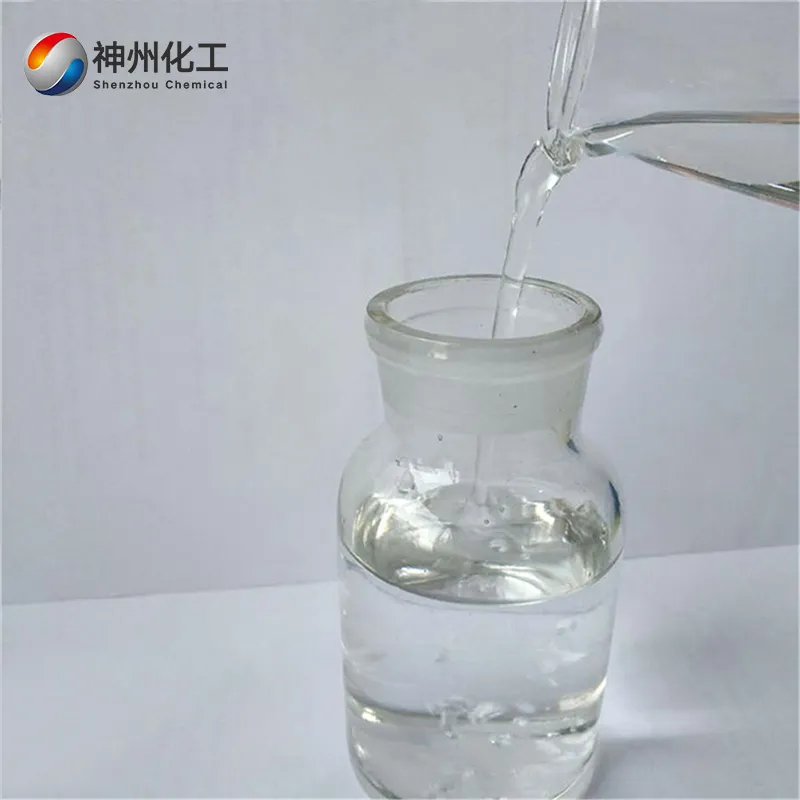
- Appearance:White crystalline powder
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available
- Chemical Name:Citric Acid Anhydrous
- CAS No.:77-92-9
- Product Categories:Food Additives
- Molecular Formula:C6H8O7
- Formula Weight:192.12
- Appearance:White crystalline powder
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available




Product Description Of Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9
Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9 is a natural component and intermediate product of physiological metabolism in animals and plants, and is also one of the most widely used organic acids in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. It is a colorless, transparent, or semi-transparent crystal, or granular, fine powder, odorless, with a strong acidic taste that is pleasant, but with a slight aftertaste. It gradually deliquesces in warm air and has slight hygroscopicity in humid air.
Natural distribution
Citric acid is widely distributed in nature, found in plant fruits such as lemons, oranges, pineapples, currants, raspberries, and grape juice, as well as in the bones, muscles, and blood of animals. Synthetic citric acid is produced by fermenting sugar-containing substances such as sugar, molasses, starch, and grapes, and can be classified into anhydrous and hydrated forms.
Pure citric acid is a colorless transparent crystal or white powder, odorless, with an appealing sour taste. The semi-transparent colorless crystals obtained from hot concentrated aqueous solutions are anhydrous, with a melting point of 153°C. The translucent colorless crystals obtained from cold aqueous solutions are the monohydrate form, with a density of 1.542. It softens at 75°C and melts at approximately 100°C.
The monohydrate form can lose water in dry air. It is a strong organic acid, soluble in water, ethanol, and ether.
It is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, soft drinks, candies, etc., and also serves as a metal cleaner, mordant, etc. Many fruits and vegetables, especially citrus fruits, contain significant amounts of citric acid, particularly lemons and limes—they contain large amounts of citric acid, with a content of up to 8% after drying (approximately 47 g/L in juice).
In citrus fruits, citric acid content ranges from 0.005 mol/L in oranges and grapes to 0.30 mol/L in lemons and limes. This content varies depending on the cultivar and growth conditions of the plant.
Chemical Properties Of Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9
| Melting point | 153-159 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 248.08°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 at 20°C |
| Bulk density | 560kg/m3 |
| Vapor density | 7.26 (vs air) |
| Vapor pressure | <0.1 hPa (20°C) |
| Refractive index | 1.493-1.509 |
| FEMA | 2306 | CITRIC ACID |
| Flash point | 100 °C |
| Storage conditions | 2-8°℃ |
| Solubility | At 15°C, citric acid is also soluble in anhydrous ethanol (76 parts citric acid per 100 parts ethanol). |
| Form | gravel |
| Acidity coefficient (pKa) | 3.14(at 20℃) |
| Color | white |
| pH value | 3.24(1 mM solution);2.62(10 mM solution);2.08(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | odourless |
| Biological origin | synthetic |
| Fragrance type | odorless |
| Explosive limit | 8%, 65°F |
| Water solubility | soluble in Water (1174g/L at 10°C, 1809g/L at 30°℃, 3825g/L at 80°C). |
| Sensitivity | Hygroscopic |
| Maximum wavelength(λmax) | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.10 |
| Merck | 142,326 |
| JECFA Number | 218 |
| BRN | 782061 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with alkalis, strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and metal nitrates. |
| InChlKey | KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.64 |
| CAS Database | 77-92-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemical Substance Information | 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-(77-92-9) |
| EPA Chemical Substance Information | Citric acid (77-92-9) |
Application of Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9
Applications in the food industry
Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9 is known as the primary food acidulant. According to China’s GB2760—1996 standard, it is permitted for use as a food acidity regulator. In the food industry, it is widely used as an acidulant, solubilizer, buffer, antioxidant, deodorizer, chelating agent, and more. Its specific applications are too numerous to list.
1. According to domestic and international statistics, the beverage industry accounts for 75% to 80% of total citric acid production. Citric acid is one of the natural components of fruit juice, not only imparting fruit flavor but also serving as a solubilizer, buffer, and antioxidant. It helps blend and harmonize components such as sugar, flavorings, and colorants in beverages, creating a balanced taste and aroma, and enhances antimicrobial preservative effects. Therefore, it is widely used in the formulation of various fruit-based soft drinks. For example, the acid content in fruit-based carbonated drinks typically ranges from 0.10% to 0.25%. For non-carbonated beverages, such as water, juice, sugar, acid, colorants, and flavorings mixtures, citric acid is used to adjust the pH to a certain acidity level, ensuring the product’s titratable acidity falls between 0.25% and 0.40%. For fruit pulp-based solid beverage powders, the addition of citric acid can be increased to 1.5% to 5.0%. In recent years, with the continuous improvement of living standards in urban and rural areas, the demand for various beverages has significantly increased. It can be predicted that the use of citric acid in the beverage industry will also significantly increase in the future.
Applications in the pharmaceutical industry
Effervescent is a widely used oral drug delivery system. When citric acid reacts with a solution of sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate, it produces a large amount of CO2 (i.e., effervescence) and sodium citrate, which can rapidly dissolve the active ingredients in the drug and enhance taste perception
For example, it enhances the solubility of laxatives and pain relievers. Citric acid syrup is a refreshing beverage for feverish patients, offering flavor correction, cooling, and detoxification benefits. Citric acid is widely used in various nutritional oral solutions, buffering the pH to 3.5–4.5 to maintain the stability of active ingredients and enhance the effectiveness of preservatives.
When combined with fruit flavorings, citric acid imparts a pleasant sour taste to mask the bitterness of medications, particularly in traditional Chinese medicine formulations. Adding 0.02% citric acid to liquid formulations forms complexes with trace amounts of iron and copper, thereby slowing the degradation of active ingredients. In chewable tablets, using 0.1%–0.2% citric acid improves the flavor of the tablets, giving them a lemon-like taste. This information was compiled and edited by Xiaonan from ChemicalBook.
Packaging Method Of Citric Acid Anhydrous 77-92-9






Factory Show