Dichloromethane 75-09-2
Have Any Questions?
Let our vertically integrated solutions – from Chinese manufacturing hubs to your local warehouse – become your competitive advantage.
- +86 13376344351
Leave Your Message
Dichloromethane 75-09-2
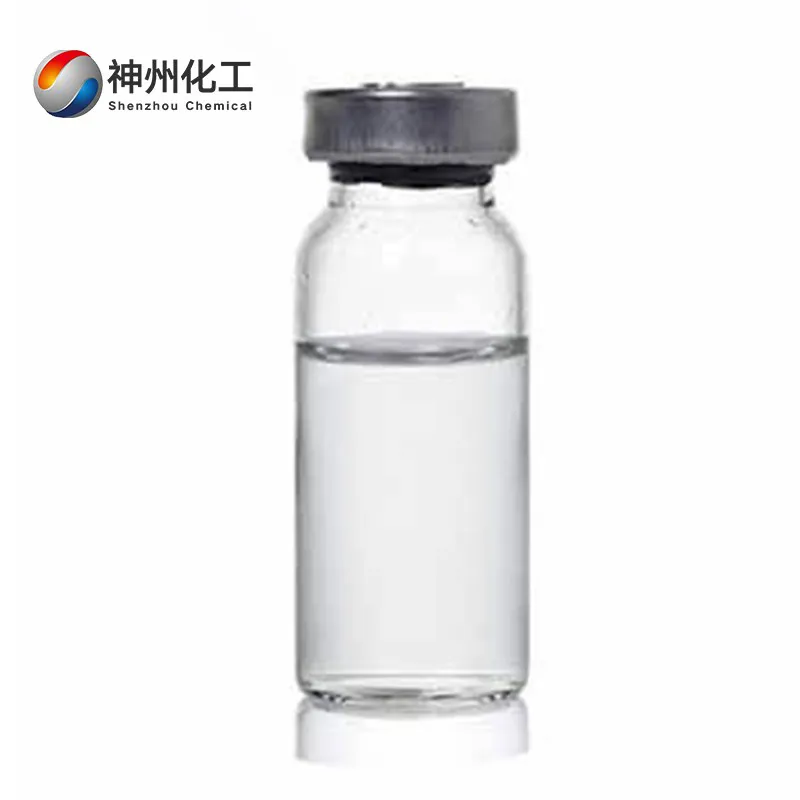

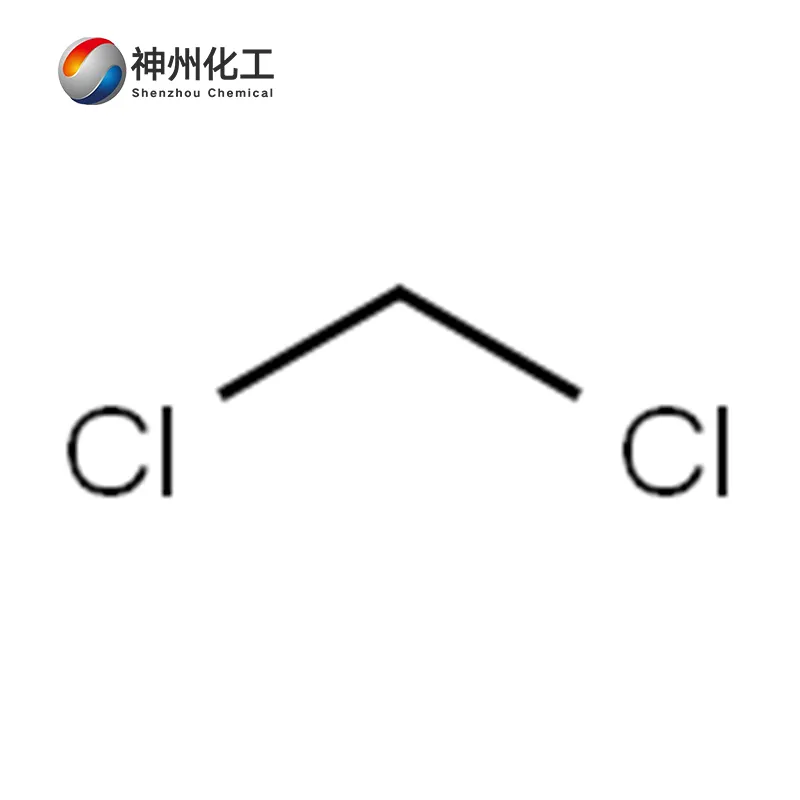


- Chemical Name:Dichloromethane
- CAS No.:75-09-2
- Product Categories:Organic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:CH2Cl2
- Formula Weight:84.93
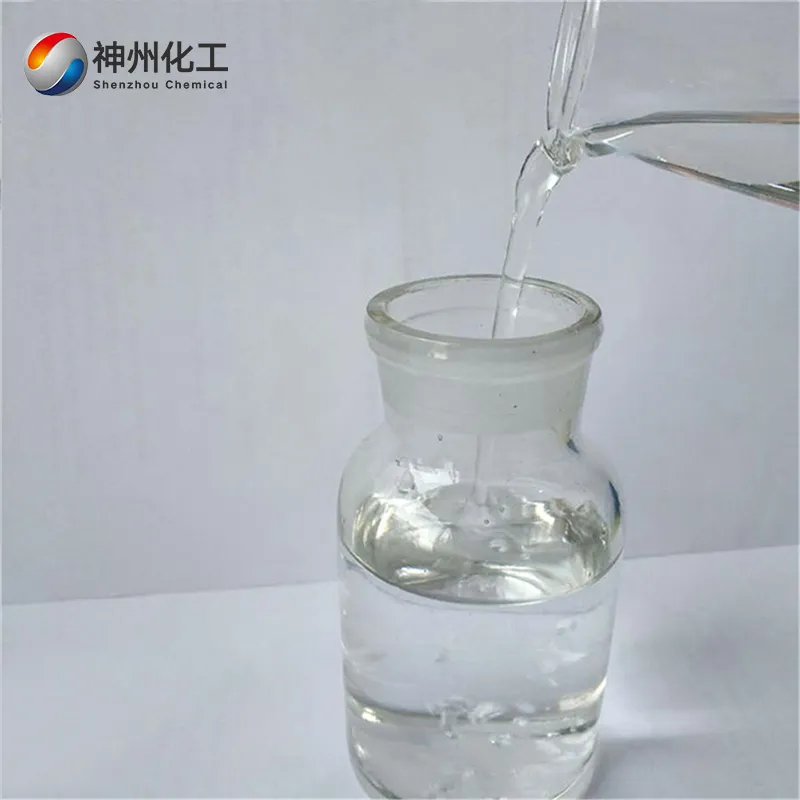
- Appearance:Colorless, transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available
- Chemical Name:Dichloromethane
- CAS No.:75-09-2
- Product Categories:Organic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:CH2Cl2
- Formula Weight:84.93
- Appearance:Colorless, transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available




Product Description Of Dichloromethane 75-09-2
Introduction
Dichloromethane is a compound formed by replacing two hydrogen atoms in a methane molecule with chlorine atoms, with the molecular formula CH₂Cl₂. It is a colorless, transparent, heavier-than-water, volatile liquid with an ether-like odor and a sweet taste.
It is non-flammable but forms an explosive mixture when mixed with high concentrations of oxygen. Dichloromethane is slightly soluble in water and miscible with most common organic solvents. It is also miscible with other chlorinated solvents, ether, ethanol, and N,N-dimethylformamide in any proportion. At room temperature, dichloromethane is poorly soluble in liquid ammonia but dissolves rapidly in phenols, aldehydes, ketones, glacial acetic acid, triethyl phosphate, formamide, cyclohexamine, and ethyl acetate. Relative density: 1.3266 (20/4°C).
Melting point: -95.1°C. Boiling point: 40°C. A non-flammable low-boiling-point solvent, it is commonly used as a substitute for flammable petroleum ether, ether, etc., and can also be used as a dental local anesthetic, refrigerant, and fire extinguishing agent, etc.
Autoignition temperature: 640°C. Viscosity (20°C): 0.43 mPa·s. Refractive index nD (20°C): 1.4244. Critical temperature: 237°C. Critical pressure: 6.0795 MPa. Upon thermal decomposition, it produces HCl and trace amounts of phosgene. When heated with water over an extended period, it forms formaldehyde and HCl. Further chlorination yields CHCl₃ and CCl₄.
Properties
Pure dichloromethane has no flash point. A solvent mixture containing equal volumes of dichloromethane and gasoline, solvent naphtha, or toluene is non-flammable.
However, when dichloromethane is mixed with acetone or methanol in a 10:1 ratio, the mixture has a flash point, and its vapor forms an explosive mixture with air, with an explosive limit of 6.2% to 15.0% (by volume).
Chemical Properties Of Dichloromethane 75-09-2
| Melting point | -97°C |
| Boiling point | 39.8-40°C mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.325 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Vapor density | 2.9 (vs air) |
| Vapor pressure | 24.45 psi (55 °C) |
| Refractive index | n20/D 1.424(lit.) |
| Flash point | 39-40°℃ |
| Storage conditions | room temp |
| Solubility | Miscible with ethyl acetate, ethanol, hexane, methanol, diethyl ether, n-octanol, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, diethyl ether, and chloroform. |
| Form | liquid |
| Color | APHA:≤10 |
| Specific gravity | 1.329 (20/20℃) |
| Odor | Odor threshold 160 to 230 ppm |
| pH value | 7 (20°C) |
| Olfactory threshold | 160ppm |
| Explosion limit values | 13-22%(V) |
| Water solubility | 20 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Maximum wavelength(λmax) | λ: 235 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 240 nm Amax: 0.20λ: 250 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.02λ: 340-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 146,063 |
| BRN | 1730800 |
| Henry’s Law Constant | 2.49 at 30 °C (headspace-GC, Sanz et al., 1997) |
| Dielectric constant | 9.1(20℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~175 mg/m3) (ACGIH); carcinogenicity: Suspected Human Carcinogen (ACGIH), Animal Sufficient Evidence, Human Inadequate Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability | Volatile |
| LogP | 1.25 |
| Surface tension | 26.5mN/m at 20°℃ |
| CAS database | 75-09-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST chemical information | Methylene chloride(75-09-2) |
| (IARC) Carcinogen classification | 2A (Vol. Sup 7,71, 110) 2017 |
| EPA chemical information | Methylene chloride (75-09-2) |
| Absorption | in accordance |
Application of Dichloromethane 75-09-2
Dichloromethane (DCM) has the advantages of strong solubility and low toxicity, and is widely used in the production of safety film, polycarbonate, and other applications such as paint solvents, metal degreasers, aerosol propellants, polyurethane foaming agents, release agents, and paint removers.
Dichloromethane is a colorless liquid used as a reaction medium in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of ampicillin, amoxicillin, and cephalosporin, among others. It is also used as a solvent in film production, a petroleum dewaxing solvent, an aerosol propellant, an organic synthesis extractant, a foaming agent for polyurethane foam plastics, and a metal cleaner.
In China, dichloromethane is primarily used in film production and the pharmaceutical industry. Film production accounts for 50% of total consumption, pharmaceutical applications account for 20% of total consumption, cleaning agents and the chemical industry account for 20% of total consumption, and other applications account for 10%.
Dichloromethane is also used as a refrigerant in industrial refrigeration systems, but it poses significant hazards. When exposed to open flames or hot objects, it can produce highly toxic phosgene. Exposure to moist air can cause hydrolysis, producing trace amounts of hydrogen chloride, and exposure to light can also promote hydrolysis, enhancing its corrosive effect on metals.
It is used for grain fumigation and in low-pressure refrigeration units and air conditioning systems. It is used as an auxiliary foaming agent in the production of polyether-type urethane foam plastics and as a foaming agent for extruded polyvinyl chloride foam plastics. Dichloromethane is also used to produce decaffeinated coffee. Coffee is first boiled to dissolve the caffeine, which floats to the surface, and then dichloromethane is used to remove the caffeine.
Applications and Functions
The primary application of dichloromethane is as a solvent. Dichloromethane possesses strong solvent properties, a low boiling point, and relatively low toxicity and reactivity, making it the most frequently used organic solvent in organic synthesis. Its role as a solvent is nearly equivalent to that of water in inorganic salt chemistry.
It is extensively used in the production of safety film, polycarbonate, and as a solvent for coatings, metal degreaser, aerosol propellant, polyurethane foam agent, release agent, and paint remover. In the pharmaceutical industry, it serves as a reaction medium for the preparation of ampicillin, amoxicillin, and cephalosporin, among others; it is also used as a solvent in film production, a petroleum dewaxing solvent, an aerosol propellant, an organic synthesis extractant, a foaming agent for polyurethane and other foam plastics, and a metal cleaner.
Due to its steric effect, dichloromethane is inert and typically does not participate in chemical reactions. However, under certain conditions, it can react. An industrial accident occurred where residual dichloromethane reacted with sodium azide in N,N-dimethylformamide to form diazomethane, causing the factory to explode. In China, dichloromethane is primarily used in film production and the pharmaceutical industry.
Film production accounts for 50% of total consumption, pharmaceuticals account for 20%, cleaning agents and the chemical industry account for 20%, and other applications account for 10%.
Packaging Method Of Dichloromethane 75-09-2






Factory Show