Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2
Have Any Questions?
Let our vertically integrated solutions – from Chinese manufacturing hubs to your local warehouse – become your competitive advantage.
- +86 13376344351
Leave Your Message
Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2
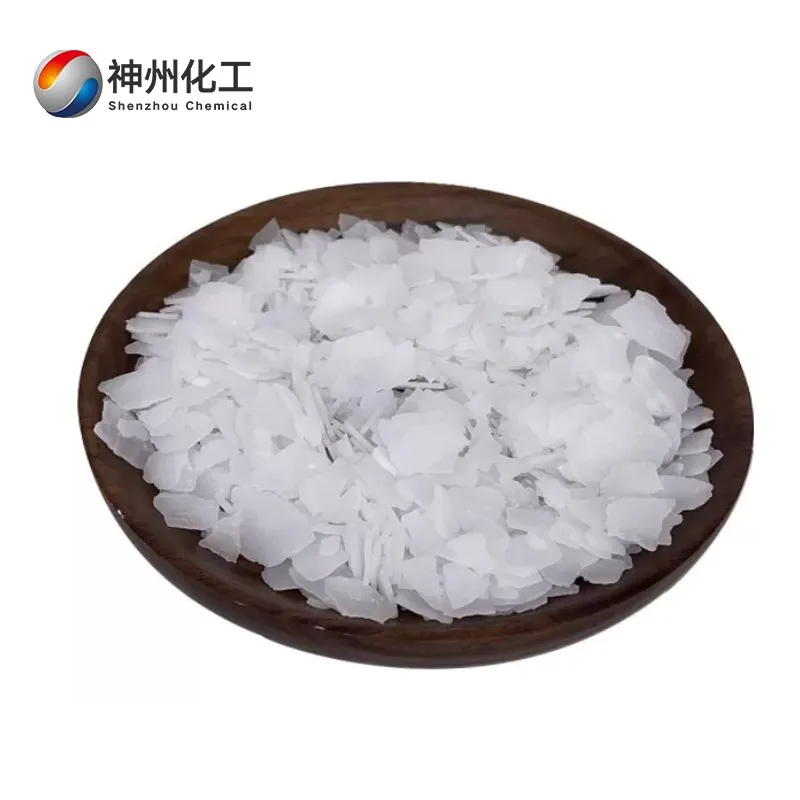
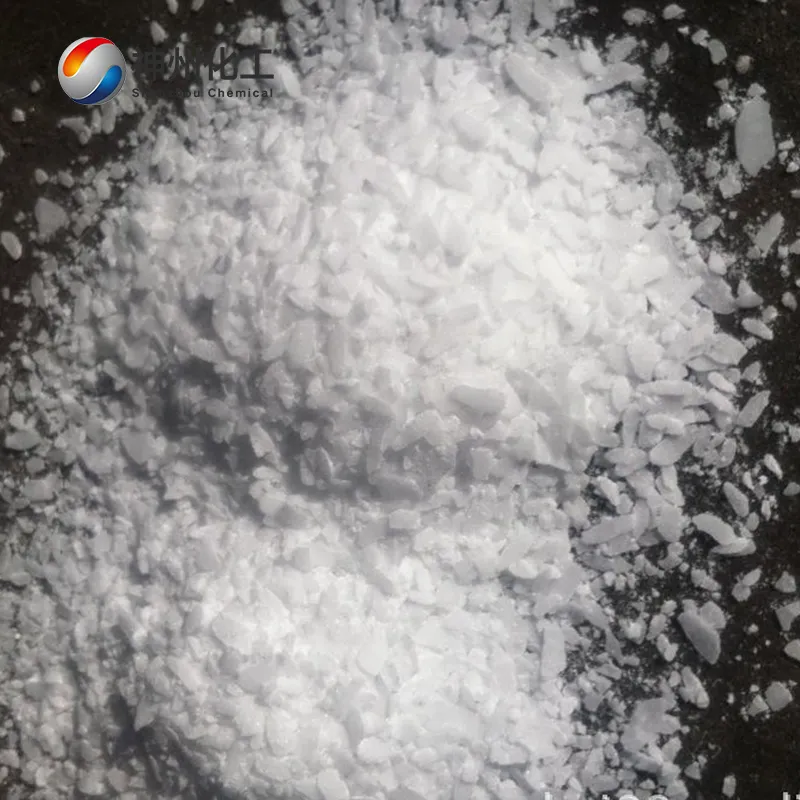
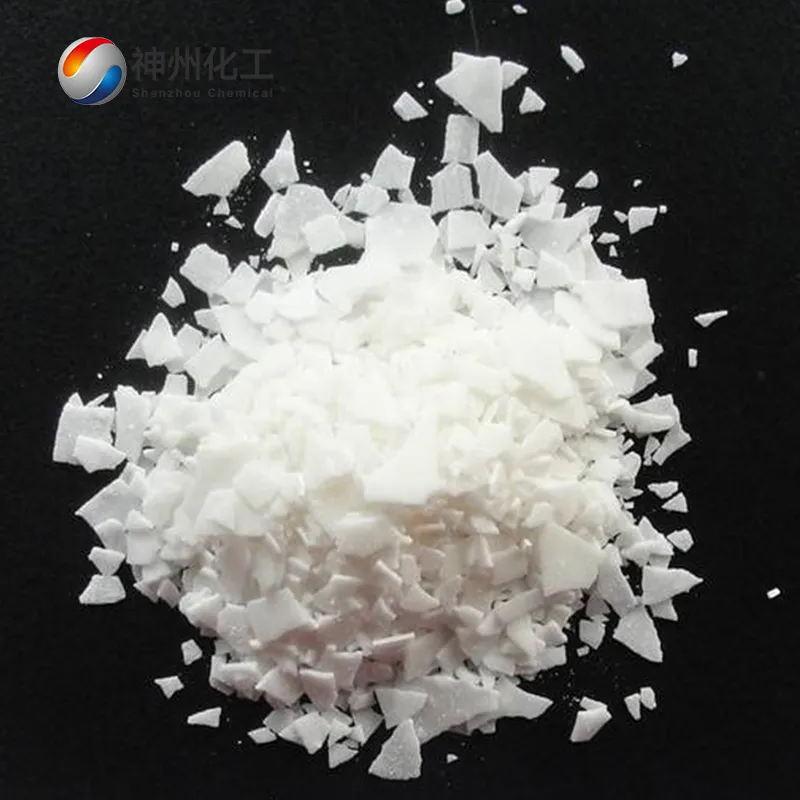

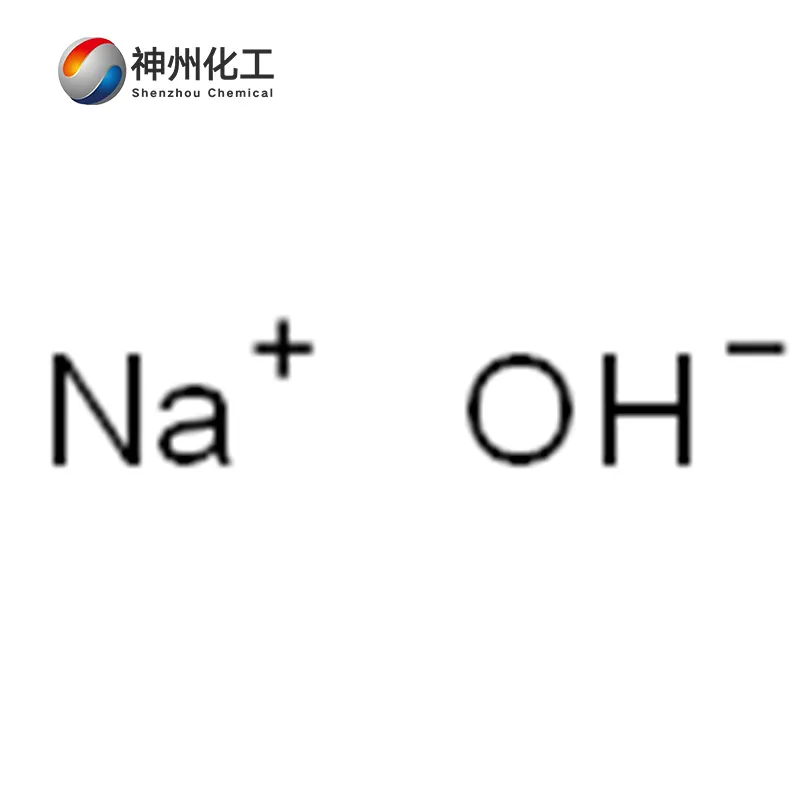


- Chemical Name:Sodium Hydroxide (solid)
- CAS No.:1310-73-2
- Product Categories:Inorganic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:NaOH
- Formula Weight:39.99711
- Appearance:White flakes/granules (99% purity)
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available
- Chemical Name:Sodium Hydroxide (solid)
- CAS No.:1310-73-2
- Product Categories:Inorganic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:NaOH
- Formula Weight:39.99711
- Appearance:White flakes/granules (99% purity)
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available




Product Description Of Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2
Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2, also known as caustic soda or lye, with the chemical formula NaOH, is a highly corrosive strong base. It typically appears as white flakes or granules and is completely soluble in water, forming an alkaline solution. It is also soluble in methanol and ethanol. This alkaline substance is hygroscopic, absorbing water vapor from the air and also absorbing acidic gases such as carbon dioxide. Sodium hydroxide is one of the most commonly used chemicals. It has a wide range of applications and is an essential component in many industrial processes: it is commonly used in the production of wood pulp paper, textiles, soap, and other cleaning agents, as well as in household alkaline drain cleaners.
Chemical Properties Of Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2
| Melting point | 681 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 1390°C |
| Density | 1.515 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Vapor density | <1 (vs air) |
| Vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 745 °C) |
| Refractive index | 1,473-1,475 |
| Flash point | 176-178°C |
| Storage conditions | room temp |
| Solubility | H2O: 1 mat at 20 °C, transparent, colorless |
| Form | beaded |
| Color | white |
| Specific gravity | 2.13 |
| pH range for acid-base indicator color change | 13 – 14 |
| pH value | 10.98(1 mM solution);11.95(10 mM solution);12.88(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | odourless |
| Water solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Maximum wavelength (wavelength) | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.015λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Decomposition | 176-178 ºC |
| Sensitivity | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 148,627 |
| Dielectric constant | 57.5(25℃) |
| Exposure limit | TLV-TWA air 2 mg/m3 (OSHA); ceiling 2 mg/m3 (ACGIH) and 2 mg/m3/15 min (NIOSH). |
| Stability | hygroscopicity |
| CAS Database | 1310-73-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemical Substance Information | Sodium hydroxide(1310-73-2) |
| EPA Chemical Substance Information | Sodium hydroxide (1310-73-2) |
Application of Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2
Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2 has a wide range of applications. In chemical experiments, it is not only used as a reagent but also serves as an alkaline desiccant due to its strong hygroscopic properties.
Caustic soda has extensive applications in the national economy, with many industrial sectors requiring it. The sector with the highest consumption of caustic soda is the production of chemical drugs, followed by the paper, aluminum smelting, tungsten smelting, artificial silk, artificial cotton, and soap manufacturing industries.
Additionally, it is used in the production of dyes, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and organic intermediates; the regeneration of old rubber; the production of metallic sodium; water electrolysis; and the production of inorganic salts, including borax, chromium salts, manganese salts, and phosphate salts.
Industrial-grade sodium hydroxide must comply with the national standard GB209-2006; Industrial-grade sodium hydroxide produced by the ion exchange membrane method should comply with the national standard GB/T11199-89; sodium hydroxide for synthetic fibers should comply with the national standard GB11212-89; and food-grade sodium hydroxide should comply with the national standard GB5175-85. In industry, sodium hydroxide is commonly referred to as caustic soda, or lye, or sodium hydroxide (Chemicalbook).
This is because concentrated sodium hydroxide solutions can cause skin burns when splashed onto the skin, as they corrode the epidermis. It has a dissolving effect on proteins and exhibits strong irritant and corrosive properties (due to its dissolving effect on proteins, alkali burns are more difficult to heal compared to acid burns). When a 0.02% solution is instilled into a rabbit’s eye, it can cause damage to the corneal epithelium.
The LD50 for mice via intraperitoneal administration is 40 mg/kg, and the LDLo for rabbits via oral administration is 500 mg/kg. Dust irritates the eyes and respiratory tract and corrodes the nasal septum; splashing onto the skin, especially mucous membranes, can cause scabs and penetrate deep tissues, leaving scars after burns; splashing into the eyes not only damages the cornea but can also cause damage to deep eye tissues, potentially leading to blindness in severe cases; Ingestion may cause digestive tract burns, colic, mucosal erosion, vomiting of bloody gastric contents, bloody diarrhea, and occasionally hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, shock, digestive tract perforation, and later gastrointestinal stricture.
Due to its strong alkalinity, it may contaminate water bodies, and precautions should be taken regarding plants and aquatic organisms.
Packaging Method Of Sodium Hydroxide (solid) 1310-73-2






Factory Show