Methanol 67-56-1
Have Any Questions?
Let our vertically integrated solutions – from Chinese manufacturing hubs to your local warehouse – become your competitive advantage.
- +86 13376344351
Leave Your Message
Methanol 67-56-1



- Chemical Name:Methanol
- CAS No.:67-56-1
- Product Categories:Organic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:CH4O
- Formula Weight:32.04
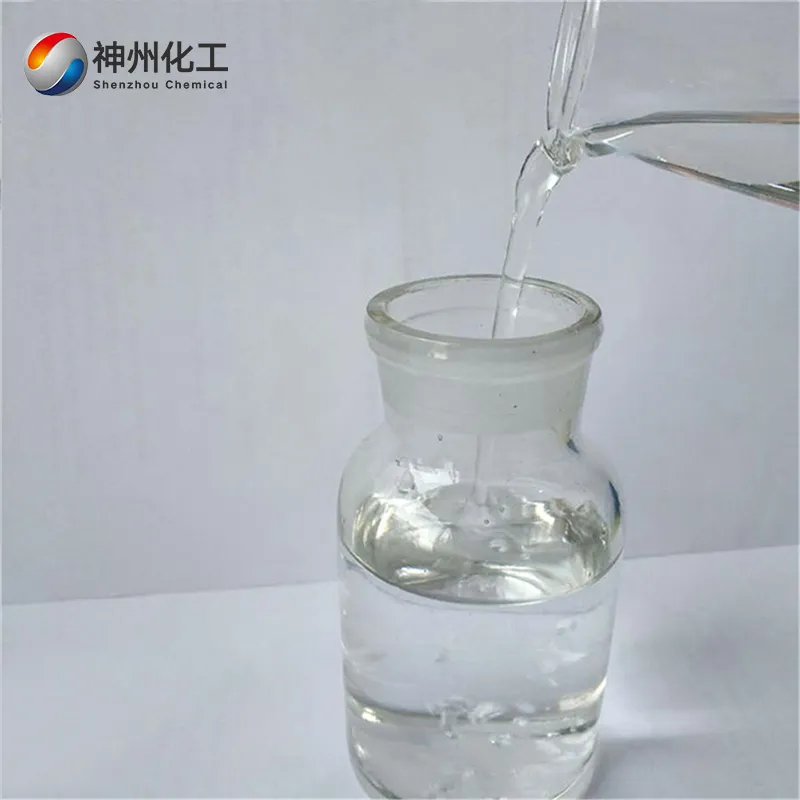
- Appearance:Colorless, transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available
- Chemical Name:Methanol
- CAS No.:67-56-1
- Product Categories:Organic Chemistry
- Molecular Formula:CH4O
- Formula Weight:32.04
- Appearance:Colorless, transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available




Product Description Of Methanol 67-56-1
Methanol 67-56-1, also known as “wood alcohol,” is an organic compound and the simplest saturated monohydric alcohol. It is a colorless, transparent, flammable, and volatile toxic liquid. Ingesting 5–10 milliliters can cause blindness, and ingesting large amounts can be fatal. At room temperature, methanol is non-corrosive to metals (except lead and aluminum) and has a slight alcohol odor. Its relative density is 0.792 (20/4°C), melting point is -97.8°C, boiling point is 64.5°C, flash point is 12.22°C, and autoignition temperature is 463.89°C. vapor density 1.11, vapor pressure 13.33 kPa (100 mmHg at 21.2°C), and the explosive limit of the vapor-air mixture is 6–36.5% (by volume). It is miscible with water, ethanol, ether, benzene, ketones, halogenated hydrocarbons, and many other organic solvents. It is commonly used as a solvent, antifreeze, fuel, or neutralizing agent.
Chemical Properties Of Methanol 67-56-1
| Melting point | -98 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 65.4 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.791 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Vapor density | 1.11 (vs air) |
| Vapor pressure | 410 mm Hg (50 °C) |
| Refractive index | n20/D 1.329(lit.) |
| Flash point | 52 °F |
| Storage conditions | 2-8°℃ |
| Solubility | Miscible with benzene |
| Acidity coefficient (pKa) | 15.2(at 25℃) |
| Form | non-particulate liquid |
| Color | colorless |
| Specific gravity | 0.793 (20/20℃) |
| Relative polarity | 0.762 |
| Odor | A faint smell of alcohol can be detected at 4 to 6000 ppm (average = 160 ppm). |
| pH value | 6.8 (20°C in H2O) |
| Flame Color | Pale blue |
| Odor Threshold | 33ppm |
| Explosion Limit | 5.5-44%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Miscible with benzene |
| Maximum Wavelength(λmax) | λ: 210 nm Amax: 0.50λ: 220 nm Amax: 0.30λ: 230 nm Amax: 0.15λ: 235 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 240 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.01λ: 400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 145,957 |
| BRN | 1098229 |
| Henry’s Law Constant | 4.99 at 25 °C (headspace-GC, Gupta et al., 2000) |
| Exposure Limit | TLV-TWA (200 ppm) (ACGIH), 260mg/m3, 1040mg/m3 (800 ppm) 15minutes (NIOSH); STEL 310mg/m3 (250 ppm); IDLH 25,000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric Constant | 33.6(20℃) |
| LogP | -0.77 |
| Surface Tension | 22.22mN/m at 298.15K |
| Surface Tension | 22.7mN/m at 20°C |
| CAS Database | 67-56-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemical Substance Information | Methyl alcohol(67-56-1) |
| EPA Chemical Substance Information | Methanol (67-56-1) |
| Absorption | in accordance |
Application of Methanol 67-56-1
Methanol 67-56-1 has a wide range of applications and serves as a fundamental organic chemical raw material and high-quality fuel. It is primarily used in the fine chemicals and plastics industries to produce various organic products such as formaldehyde, acetic acid, chloroform, methylamine, and dimethyl sulfate, and is also an important raw material for pesticides and pharmaceuticals. After further processing, methanol can be used as a new type of clean fuel and can also be blended with gasoline for combustion.
Methanol oxidation to formaldehyde
Methane is directly oxidized into formaldehyde under high temperatures in the presence of pumice silver, a catalyst, or other solid catalysts. Currently, over 40% of global methanol production is used for formaldehyde synthesis, which is further processed into resins, plastics, and other chemical raw materials. Polyformaldehyde is an engineering plastic with excellent performance and a wide range of applications. Formaldehyde is also used to produce nearly 100 downstream products, including butanediol and urea.
Methylamine Production from Methanol Ammoniation
Methylamine is produced by mixing methanol with ammonia in a specific ratio, then synthesizing the mixture at temperatures of 370–420°C and pressures of 5.0–20.0 MPa using activated alumina as a catalyst. This process yields a mixture of methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine, which can be further purified by distillation to obtain pure methylamine, dimethylamine, or trimethylamine products. Methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine are used in pesticides, pharmaceuticals, dyes, or as organic raw material intermediates. Under the presence of metal silicon-aluminum catalysts or ZSM-5 molecular sieves, methanol can be dehydrated to produce dimethyl ether.
Methylaldehyde is produced by dehydrogenation of methanol.
Methyl formate is an organic synthesis raw material and can be used to produce methylamide, dimethylformamide, etc. Methylamide is a raw material for pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and dyes, and can also be used as a paper treatment agent, a softener in the fiber industry, and a polar solvent in organic synthesis. Dimethylformamide is an important organic chemical raw material and an excellent solvent, used in applications such as gas absorption agents, pesticides, polyurethane synthetic leather, polyacrylonitrile filament production, and butadiene extraction.
Applications
Methanol readily undergoes esterification reactions with sulfuric acid and carbonic acid; at 0°C, it does not readily react with hydrochloric acid. At 160°C, in the presence of sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, or boric acid, methanol can lose water to form methyl ether (CH₃-O-CH₃). Methyl alcohol vapor can also lose water to form ether when passed through aluminum oxide or thorium oxide (at temperatures of 200°C and 400°C, respectively). Methanol can be used as a solvent; metal halides and organic acid salts are more or less soluble in methanol, while sulfates have extremely low solubility and carbonates are completely insoluble in methanol. Methanol is also a raw material for the production of formaldehyde, formic acid, and inorganic or
Packaging Method Of Methanol 67-56-1






Factory Show