Acetic Acid 64-19-7
Have Any Questions?
Let our vertically integrated solutions – from Chinese manufacturing hubs to your local warehouse – become your competitive advantage.
- +86 13376344351
Leave Your Message
Acetic Acid 64-19-7



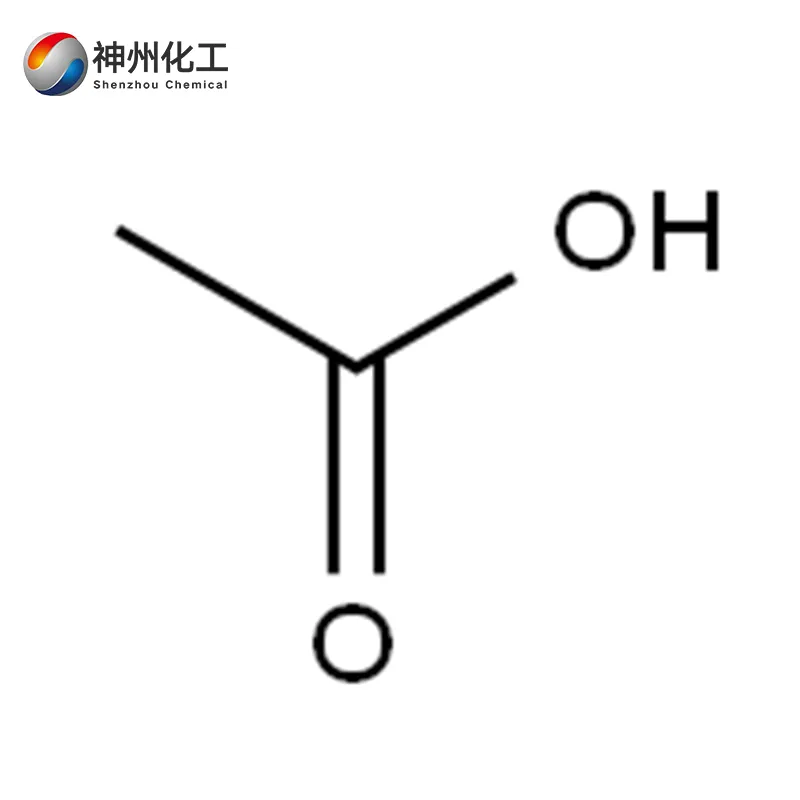
- Chemical Name:Acetic Acid 64-19-7
- CAS No.: 64-19-7
- Product Categories:Chemical Reagents
- Molecular Formula:C2H4O2
- Formula Weight:60.05
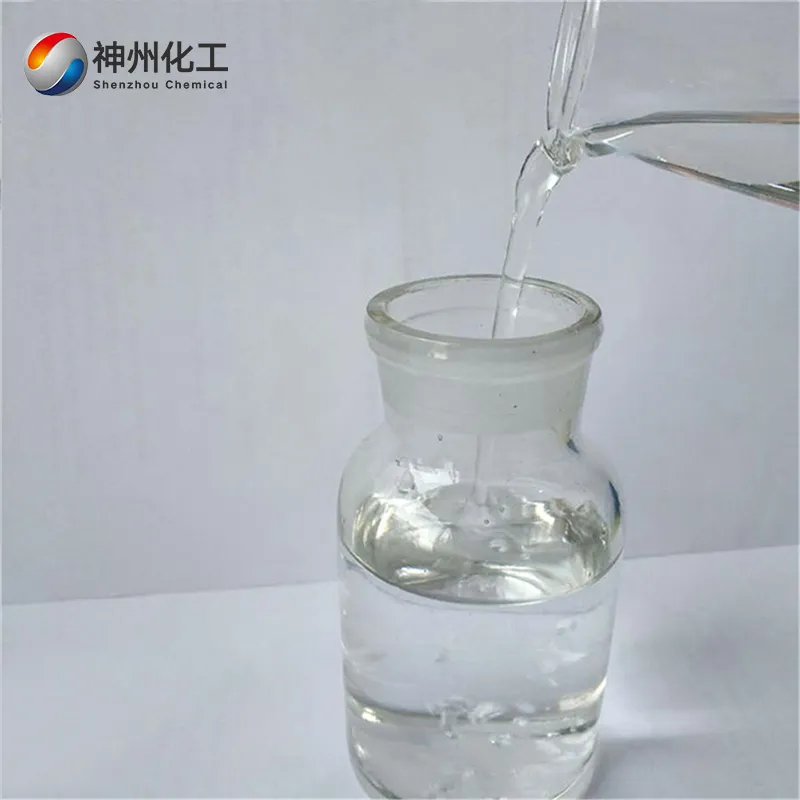
- Appearance:Transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available
- Chemical Name:Acetic Acid 64-19-7
- CAS No.: 64-19-7
- Product Categories:Chemical Reagents
- Molecular Formula:C2H4O2
- Formula Weight:60.05
- Appearance:Transparent liquid
- Storage and transportation characteristics: low temperature, ventilation, dryness, waterproof, moisture-proof
- Type Of Transportation:By Air/By Sea/By Train/By Express
- Type Of Transportation:Available




Product Description Of Acetic Acid 64-19-7
Acetic acid, commonly known as vinegar acid (AcOH), is named after its primary component in vinegar and is one of the most important fatty acids. In nature, it typically exists in free form or as an ester in many plants.
Its molecular formula is CH₃COOH. The production and use of vinegar have a history of thousands of years. There are records of vinegar production in ancient China. However, concentrated acetic acid was first successfully synthesized by Stahl in 1700.
Pure acetic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It has a melting point of 16.6°C, a boiling point of 117.9°C, and a relative density of 1.049 (20/4°C). It is soluble in water, ethanol, glycerol, ether, and carbon tetrachloride; it is insoluble in carbon disulfide. Anhydrous acetic acid solidifies into an ice-like substance at low temperatures, commonly known as glacial acetic acid.
It is corrosive. As a weak organic acid, it exhibits the general properties of acids and can undergo esterification reactions with alcohols.
Chemical Properties Of Acetic Acid 64-19-7
| Melting point | 16.2 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point | 117-118 °C(lit.) |
| density | 1.049 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.07 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 11.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.371(lit.) |
| FEMA | 2006 | ACETIC ACID |
| Fp | 104 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | alcohol: miscible(lit.) |
| form | Solution |
| pka | 4.74(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.0492 (20℃) |
| color | colorless |
| PH | 3.91(1 mM solution);3.39(10 mM solution);2.88(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Strong, pungent, vinegar-like odor detectable at 0.2 to 1.0 ppm |
| PH Range | 2.4 (1.0M solution) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.006ppm |
| Odor Type | acidic |
| explosive limit | 4-19.9%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.02 λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 500 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| JECFA Number | 81 |
| Merck | 14,55 |
| BRN | 506007 |
| Henry’s Law Constant | 133, 122, 6.88, and 1.27 at pH values of 2.13, 3.52, 5.68, and 7.14, respectively (25 °C, Hakuta et al., 1977) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm ~25 mg/m3) (ACGIH, OSHA, and MSHA); TLV-STEL 15 ppm (37.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.1(2℃) |
| Stability: | Volatile |
| LogP | -0.170 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 64-19-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid(64-19-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid (64-19-7) |
Application of Acetic Acid 64-19-7
Mainly used for the preparation of acetic anhydride, vinyl acetate, acetate esters, metal acetates, chloroacetic acid, cellulose acetate, etc., and also serves as a solvent
Used in the synthesis of vinyl acetate, cellulose acetate, acetate esters, metal acetates, and halogenated acetic acids, it is also an important raw material for pharmaceuticals, dyes, pesticides, and organic synthesis
Commonly used as an analytical reagent, general-purpose solvent, non-aqueous titration solvent, and chromatographic reagent. It is also used in organic synthesis. Used as an acidulant, it can be used in compound seasonings, vinegar, canned foods, jellies, and cheeses, with usage adjusted according to production needs. It can also be used as a flavoring agent in aromatic wines, with a usage rate of 0.1–0.3 g/kg.
Acetic acid is a bulk chemical product and one of the most important organic acids. It is primarily used in the production of vinyl acetate, acetic anhydride, acetate esters, and cellulose acetate. Polyvinyl acetate can be made into films and adhesives and is also a raw material for synthetic fibers such as viscose. Acetate cellulose can be used to manufacture artificial silk and motion picture film. Acetates formed from lower alcohols are excellent solvents and are widely used in the paint industry. Acetic acid is an excellent solvent for oxidation reactions (e.g., for the oxidation of para-xylene to produce terephthalic acid).
Acetic acid is an important raw material in the organic synthesis industry, used to synthesize acetic anhydride, diethyl malonate, ethyl acetate, halogenated acetic acids, etc., and can also be used to manufacture drugs such as aspirin and pesticides like 2,4-D. It is also used in the production of acetate salts, such as salts of manganese, sodium, lead, aluminum, zinc, and cobalt, which are widely used as catalysts, auxiliaries in textile dyeing, and leather tanning industries. For example, aluminum acetate is a mordant, a disinfectant, and an astringent in medicine; lead acetate is used as lead white in paint colors; and lead tetraacetate is an organic synthesis reagent.
It can oxidize 1,2-diols into aldehydes or ketones; sodium acetate and potassium acetate are widely used as buffers in biochemistry. In the food industry, acetic acid is used as an acidifier, flavor enhancer, and flavoring agent. When manufacturing synthetic vinegar, acetic acid is diluted with water to a concentration of 4-5%, and various flavorings are added. The flavor is similar to that of traditionally brewed vinegar, but the production time is shorter and the cost is lower. Acetic acid has strong corrosive properties.
It can cause skin irritation and blistering. It is classified as a secondary organic acid corrosive substance. Its primary uses include the preparation of acetic anhydride, vinyl acetate, acetate esters, metal acetates, chloroacetic acid, and cellulose acetate, which are used in the production of ethyl acetate, food flavorings, and wine flavorings. It is also used as an analytical reagent, solvent, and cleaning agent, and is a commonly used organic acid. Applications include analysis, solvents, organic synthesis, and the preparation of buffers. It is also used as a catalyst for dyeing solutions and as an auxiliary material.
Packaging Method Of Acetic Acid 64-19-7






Factory Show